Vaughan
| Vaughan | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| — City — | |||
| City of Vaughan | |||
 |
|||
|
|||
| Motto: The City above Toronto | |||
 |
|||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | |||
| Province | |||
| Regional Municipality | York | ||
| Communities |
List of mayor subdivisions
|
||
| Settled | 1792 | ||
| Incorporated | 1850 (Township) | ||
| Incorporated | 1991 (City) | ||
| Government | |||
| - Type | Municipal (City) | ||
| - Mayor | Linda Jackson | ||
| - Regional Councillor | Joyce Frustaglio Mario Ferri Gino Rosati |
||
| - City Manager | Clayton D. Harris | ||
| - Councillors |
List of ward councillors
|
||
| - MPs, and MPPs |
List of MPs
List of MPPs
|
||
| Area(From Statistics Canada) | |||
| - Land | 273.58 km2 (105.6 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2006)From Statistics Canada | |||
| - Total | 238,866 | ||
| - Density | 873.1/km2 (2,261.3/sq mi) | ||
| - Total Private Dwellings | 71,265 | ||
| Population ranked 18th nationally | |||
| Time zone | EST (UTC-5) | ||
| - Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) | ||
| Area code(s) | 905 and 289 | ||
| Website | www.vaughan.ca | ||
Vaughan (pronounced /ˈvɑːn/ Vahn) (2006 population 238,866)[1] is a city in York Region north of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Vaughan is one of the fastest growing municipalities in Canada,[2] having nearly doubled in population since 1991. Vaughan is located in Southern Ontario and is part of the Greater Toronto Area.
Contents |
History
The first European to pass through Vaughan was the French explorer Étienne Brûlé, who traversed the Humber Trail in 1615. However, it was not until the townships were created in 1792 that Vaughan began to see any settlements, as it was considered to be extremely remote and the lack of roads through the region made travel difficult. The township was named after Benjamin Vaughan, a British commissioner who signed a peace treaty with the United States in 1783.
Despite the hardships of pioneer life, settlers came to Vaughan in considerable numbers. The population grew from 19 men, 5 women, and 30 children in 1800 to 4300 in 1840. The first people to arrive were mainly Pennsylvania Germans, with a smaller number of families of English descent and a group of French Royalists being represented. This migration from the United States was by 1814 superseded by an influx of immigrants from Britain. While many of their predecessors had been agriculturalists, the newer immigrants proved to be highly skilled tradespeople, which would prove useful for a growing community.
Around the facilities established by this group arose a number of hamlets, the oldest of which was Thornhill, which witnessed the construction of a saw-mill in 1801, a grist mill in 1815, and boasted a population of 300 by 1836. Other such enclaves included Kleinburg, Coleraine, Maple, Richmond Hill, Teston, Claireville, Pine Grove, Carrville, Patterson, Burlington, Concord, Edgeley, Fisherville, Elder's Mills, Elgin Mills, Jefferson, Nashville, Purpleville, Richvale, Sherwood, Langstaff, Vellore, and Burwick (Woodbridge).
Vaughan changed relatively little in its early history, from the 1840s when the number of inhabitants stood at 4300 to 1935 when it had 4873 residents. However, World War II sparked an influx of immigration, and by 1960 the population stood at 15,957. As well, the ethno-cultural composition of the area began to change with the arrival of different groups such as Italians, Jews and Eastern Europeans.
Incorporated in 1850 as Vaughan Township, a municipal government was established. Vaughan Road was a rural road constructed in 1850 that linked Vaughan Township with Toronto, though this street's current alignment is much shorter and serves only much of the eastern half of the former city of York.[3] In 1971, the new regional government of York Region was established, acquiring policing and welfare services from the communities it served; simultaneously, the township merged with the Village of Woodbridge to form the Town of Vaughan. In 1991, it officially changed its legal status to City of Vaughan.[4]
An F2 tornado tore through the city of Vaughan during the Southern Ontario Tornado Outbreak on August 20, 2009. Premier Dalton McGuinty and Vaughan mayor Linda Jackson toured the destruction the next day and reported 200 homes in critical shape and as many as 600 additional homes likely to be demolished. Many people were, and as of January 2010, are still displaced. This list includes the Giovannettis and the Mancinis.[5] It also ripped up trees, flipped cars, and left thousands of people without power. Vaughan declared a state of emergency because of the widespread damage.[6][7] One man injured in the storm suffered a heart attack the following morning.[5] Fortunately there were no deaths reported.
Law and government
Even though Vaughan is a city, it is not in the phone book. Instead, its constituent communities are still listed separately in the Yellow Pages directory and White Pages.
Vaughan is the first municipality in Ontario to have a Youth City Councillor. The youth city councillor is appointed as a non-voting member of Council every six months to represent the youth of Vaughan. Vaughan council originally rejected the proposal of a youth councillor but after the Vaughan Youth Cabinet amended their proposal, Council accepted the recommendation.[8]
The City of Vaughan's Council is made up of nine members; a mayor, three regional councillors and five local councillors. The mayor, elected at large by electorate, is the head of Vaughan council and a representative on York Region Council. The three regional councillors are elected to represent Vaughan at both local and regional levels of government. Five local councillors are elected, one from each of Vaughan's five wards, to represent those wards on Vaughan Council. City councillors meet at the Civic Centre, located in the community of Maple. Construction recently began on a new city hall, to be called the Lorna D. Jackson Civic Centre in memory of the late Mayor. The new Civic Centre will be one of the first in Canada to conform to a LEED Gold Standard, the second highest environmental classification available.[9] The Toronto Star newspaper has made claims that the naming was part of a preliminary deal that would wrap up an outstanding lawsuit between the Jackson estate and the city.
Reports are Vaughan will have a credit card backed by the city that rewards purchases with lower property taxes.[10]
Mayor
Following the death of mayor Lorna Jackson in 2002, Michael Di Biase was appointed mayor by Vaughan council by virtue of his position as one of two regional councillors representing Vaughan, Joyce Frustaglio was the other regional councillor. Gino Rosati, a Vaughan local councillor, was subsequently appointed by Vaughan Council to fill Di Biase’s position as regional councillor and a by-election was held to fill Rosati’s local councillor’s position which was won by Linda Jackson (the daughter of former mayor Lorna Jackson). Di Biase became involved in the city's politics when he was elected local councillor in 1985. In the 2003 Municipal Election, Di Biase won his first official term since Jackson's passing.
In the municipal election on November 13, 2006, Di Biase was narrowly defeated by Linda Jackson, who was sworn in as mayor on December 4, 2006.
On June 18, 2008, an audit of Jackson's 2006 campaign finances found that the politician exceeded her legal spending limit of $120,419 by at least $12,356, or 10 per cent. The auditors, LECG Canada Ltd., say that amount could almost double if what they believed to be unreported contributions in kind at various election events – but couldn't prove – are later verified.[11]
They also found found other apparent contraventions of the Canada Elections Act, including at least five instances where associated companies made donations that exceeded the normal $750 donation limit per company.
On 24 June 2008, Vaughan Council voted unanimously to hire a special prosecutor to consider laying charges against Jackson under the Municipal Elections Act in reaction to the auditors' report. Council hired Timothy Wilkin, "an expert in municipal law" to decide what (if any) charges are to be laid.[12] If Jackson is charged and found guilty, she would face punishments ranging from fines to removal from office.
Subsequently an audit was conducted on former Mayor DiBiase;s 2006 election campaign funds. This exposed 27 contraventions under the Elections Act, along with a $155,000 anonymous cash payment made to his lawyer to cover his legal fees. Mr. DiBiase has refused to disclose who made this payment.[13] His court case will be heard in November 2009.
Geography
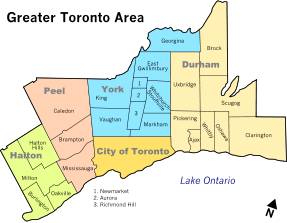
Vaughan is bounded by Caledon, Ontario and Brampton, Ontario to the west, King, Ontario and Richmond Hill, Ontario to the north, Markham, Ontario and Richmond Hill, Ontario to the east, and Toronto, Ontario to the south. It is located at .
Health care
Vaughan is the largest city in Canada without a hospital within its city boundaries.[14] The nearest full-service hospital facilities are Humber River Regional Hospital, to the south in Toronto, and York Central Hospital to the east in Richmond Hill.
There is a new hospital proposed along Major Mackenzie Drive (between Highway 400 and Jane Street) [15] which would serve Vaughan and planning stage began in 2007.[16] However, it is unlikely that construction would begin on the hospital until at least 2013.[17]
Community boundaries
There are five communities that make up the city of Vaughan.
- Woodbridge, Ontario, North/South - Teston/Steeles, East/West - Hwy 400/Hwy 50
- Maple, Ontario, North/South - King Vaughan Line/Rutherford, East/West - Bathurst/Hwy 400
- Thornhill, Ontario, North/South - Rutherford/Steeles, East/West - Yonge/Dufferin
- Concord, Ontario, North/South - Rutherford/Steeles, East/West - Dufferin/Hwy 400
- Kleinburg, Ontario, North/South - Kirby/Major Mac, East/West - Pine Valley/Hwy 50
Transportation
Demographics
| Ethnic Origin[3] | Population | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| Italian | 79,835 | 43.96% |
| Jewish | 33,705 | 16.90% |
| Canadian | 18,950 | 10.43% |
| English | 9,345 | 5.14% |
| East Indian | 8,930 | 4.91% |
| Chinese | 7,435 | 4.09% |
| Russian | 6,490 | 3.36% |
| Polish | 5,855 | 3.22% |
| Irish | 5,635 | 3.10% |
| Black | 3,580 | 1.97% |
Vaughan is one of southern Ontario's fastest growing cities. According to Statistics Canada, the population grew 37.3[4] percent in a mere four year period (more than 9.3% annually), and also has a young age profile than the Canadian average as 22.3 percent is under the age of 14, while those over 65 constitute 8.15%, one of the lowest in Ontario resulting in an average age of 34.1.
Vaughan is reputably known as having some of the highest concentrations of southern Europeans (notably Italians), Eastern Europeans (chiefly Russians and Poles) and Jewish people in Ontario, while those who are of British and/or Irish origin form a smaller proportion than in many other southern Ontario cities.
Visible minorities make up 26.6% of the population.[18] Vaughan has a small but growing Indian, Pakistani, Hispanic, Jamaican, Vietnamese and Chinese population.
Residents of Vaughan are fairly religious; the city has the lowest number of non-affiliates in Ontario. Some 67.42% of the population adheres to Christianity, mostly Roman Catholicism (55.80%). Those who practice non-Christian religions adhere to, in order of size, Judaism (18.20%), Hinduism (2.47%), Islam (2.43%), and Buddhism (0.56%).
Attractions
- Boyd Conservation Area, park located between Woodbridge and Kleinburg.
- Canadian Soccer Hall of Fame and Museum
- Canada's Wonderland, Canada's largest amusement park located in Maple.
- McMichael Canadian Art Collection, located in Kleinburg.
- Thornhill Town Centre, Vaughan's pedestrian friendly town centre located in Thornhill.
- Vaughan Mills, a large mall in the Greater Toronto Area, was constructed in Vaughan in 2004.
- J.E.H. MacDonald House
Education
York University in North York, Ontario lies on the Toronto side of the Toronto-Vaughan border. It is a major comprehensive university, with more than 43,000 students enrolled through ten different faculties. There are also a number of Elementary and High Schools in Vaughan which operate under the York Region District School Board and the York Catholic District School Board.
Twin cities
 Sora, Italy (1992)
Sora, Italy (1992) Ramla, Israel (1993)
Ramla, Israel (1993) Sanjo, Japan (1993)
Sanjo, Japan (1993) Yangzhou, China (1995)
Yangzhou, China (1995) Baguio, Philippines (1997)
Baguio, Philippines (1997) Delia, Italy (1998)
Delia, Italy (1998) Lanciano, Italy (2002)
Lanciano, Italy (2002) Riga, Latvia (1968)
Riga, Latvia (1968)
Sports
- Vaughan is home to the Ontario Soccer Association. The OSA is the largest sports organization in Canada, with over 500,000 registered players. It is also home to the Canadian Soccer Hall of Fame and Museum.
- Woodbridge Softball Association
- Italia Shooters - Canadian Soccer League 2006 Champions
- Toronto Canada Moose - a Tier II Junior "A" ice hockey team based out of the community of Thornhill (Vaughan/Markham), Ontario. They are a part of the Greater Metro Junior 'A' Hockey League.
- Vaughan Vipers - a Tier II Junior "A" ice hockey team. They are a part of the Ontario Provincial Junior A Hockey League.
- Vaughan Flames - a top level women's ice hockey team. They are members of the Canadian Women's Hockey League.
- The Sports Village - a large sports facility in Maple.
- Vaughan Rangers - member organization of the GTHL, operates junior hockey programs.
- Vaughan Kings - GTHL hockey team
- Vaughan Vikings - Baseball programs for ages 4 to 21 years old.
- Vaughan Stars Diving Club - Teaches competitive diving for children and adults.
Media
- Vaughan Citizen
- Vaughan Today
- Vaughan Weekly
- OnVaughan.com
References
- ↑ "Community highlights for Vaughan". 2006 Community Profiles. Statistics Canada. http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/profiles/community/Details/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo1=CSD&Code1=3519028&Geo2=PR&Code2=35&Data=Count&SearchText=vaughan&SearchType=Begins&SearchPR=01&B1=All. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ "Changes in population at the community level". A profile of the Canadian population: where we live. Statistics Canada. 2003-01-20. http://geodepot.statcan.ca/Diss/Highlights/Page12/Page12_e.cfm. Retrieved 2006-10-29.
- ↑ "History of Vaughan Road". The Tollkeepers Cottage and Early Roads such as Vaughan Road. http://www.lostrivers.ca/points/vaughanrd.htm. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ Bulletin #4: Settlement, Education, Social and Political History. City of Vaughan Archives, Cultural Services Division. 1992.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Roberts, Rob (2009-08-21). "Vaughan man suffers heart attack after tornado injuries; McGuinty visits damaged neighbourhood". National Post. http://network.nationalpost.com/np/blogs/toronto/archive/2009/08/21/vaughan-man-suffers-heart-attack-after-tornado-injuries-mcguinty-visits-damaged-neighbourhood.aspx. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ↑ "'Miracle no one killed' by Vaughan tornado, mayor says". Vaughan Citizen. 2009-08-20. http://www.yorkregion.com/article/95771. Retrieved 2009-08-21.
- ↑ Relief and disbelief in Vaughan
- ↑ Youth in Politics Article
- ↑ "Vaughan Highlights Environmental Partnerships at 2006 Smog Summit". 2006-06-07. http://www.city.vaughan.on.ca/newscentre/2006/news06-079.cfm. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ Liu, Karon (2007-09-12). "Vaughan credit card greeted with skepticism". National Post. http://www.canada.com/nationalpost/news/toronto/story.html?id=1a0c200d-bf65-4210-b519-ca25df778b91. Retrieved 2008-02-19.
- ↑ Vaughan mayor to face election-financing charges CBC News 25 June 2008
- ↑ Vaughan mayor faces charges over election Phinjo Gombu, Toronto Star 25 June 2008.
- ↑ Former Vaughan mayor Di Biase faces 27 election-related charges Caroline Grech, Yorkregion.com 17 Sept 2009
- ↑ Ontario starts planning for new hospital in Vaughan
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ Vaughan hospital delays 'frustrating'
- ↑ http://www12.statcan.ca/english/census06/data/highlights/ethnic/pages/Page.cfm?Lang=E&Geo=CSD&Code=35&Table=1&Data=Count&StartRec=1&Sort=2&Display=Page&CSDFilter=5000
External links
 |
Caledon | King | Richmond Hill |  |
| Brampton | Markham | |||
| Toronto |
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||